Using high-performance computing, ANTAREX researchers have demonstrated a breakthrough approach that scales up and accelerates the discovery of novel drugs.
The ANTAREX team’s approach is based on exascale-ready high-performance computing that they’ve applied to accelerating drug discovery. Using a 10 petaflop Marconi Intel Xeon Phi supercomputer – ranked the 19th most powerful computer in the world on the November 2018 TOP500 list – the ANTAREX partners focused on the real-life case of the Zika pandemic crisis.
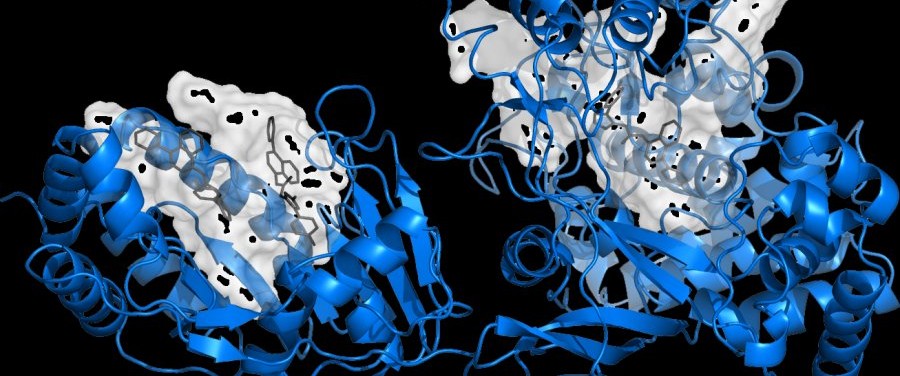
In the Zika case study, the ANTAREX team, coordinated by Prof. Cristina Silvano in collaboration with prof. Gianluca Palermo, identified 26 binding sites from the crystal structures of 5 Zika proteins: NS5, NS1, NS2B/NS3, NS3 and the envelope protein. A total of 1.2 billion molecules were tested via computer simulation on 1 million computational threads on the Marconi supercomputer. This makes it the largest virtual screening experiment ever launched in terms of computational threads and compound database size.
ANTAREX (AutoTuning and Adaptivity appRoach for Energy efficient eXascale HPC systems) also focused on a second scenario involving the mitigation of traffic congestion in smart cities using a self-adaptive navigation system. The project ended in November 2018.
For more information, please see:
ANTAREX project website (www.antarex-project.eu)
ANTAREX4ZIKA project web page (www.antarex4zika.eu)
Link to CORDIS new: https://cordis.europa.eu/news/rcn/131009/en?WT.mc_id=exp
